Dr. Howard Tenenbaum's brilliant research as reported by 2ND SMARTEST GUY IN THE WORLD: "Possible Treatment Approach for Management of Post-COVID Vaccination Myocarditis"
Dr. Tenenbaum proposes treating myocarditis with a combination of doxycycline, ivermectin, zinc and resveratrol. a low dose of doxycycline could prove to be a preventative measure for myocarditis
‘This is perhaps the most important article in this Substack’s ongoing series exposing the Modified mRNA slow kill bioweapon, and the various associated “vaccine”-induced death and disease mitigation strategies incorporating inexpensive repurposed drugs that actually work.
Today’s article focuses on the growing tsunami of cardiovascular-related deaths due to the Covid-19 “vaccine.” Fortunately, there is now credible evidence that the combination of doxycycline and ivermectin can radically ameliorate this heart damage, thus preventing a majority of deaths related to these cardiomyopathy-type injuries.
The recent discovery of low dose doxycycline can protect the heart in undiagnosed, or sub-clinical heart injuries; in other words, those that received the “vaccines” would all hugely benefit from this approach.
For diagnosed cases of myocarditis, a combination therapy of regular dose of doxycycline and ivermectin may slow down, and even reverse the damage.
We are currently in wholly uncharted territory when it comes to the treatment duration, and there is no data as of this writing to indicate how long this combination therapy should be administered.
According to the popular narrative, the cause of the recent tsunami of myocarditis is the SARS-CoV-2 viral infection; however, this narrative is incorrect as evidenced by a large population-based study of post-Covid-19 unvaccinated patients who suffered from Covid-19. The study involving 196,992 adults, all members of Clalit Health Services in Israel, did not show an increased incidence of either pericarditis or myocarditis among this cohort.
A research paper titled Cardiovascular Manifestations of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 vaccine in adolescents was published in Aug 2022. The study involved 301 vaccinated adolescents from two schools in Thailand. 29% of the participants showed cardiovascular stress signs, including tachycardia, shortness of breath, palpitations, chest pain, and hypertension, and 2.3% of the participants exhibited at least one elevated cardiac biomarker.
The attempt was made by the researchers to diminish these alarming results, by stating that the myocarditis experienced by the participants were temporary and mild, with all cases fully recovering within 14 days. What the paper failed to mention is that
myocarditis is almost never temporary or mild.
We also have data showing no increases in myocarditis during the height of the “pandemic,” but ever since the “vaccine” rollout cases have surged to unprecedented levels, as have turbo cancers, etc.
The truth is that people who have received the Covid-19 injections are subject to continuous autoimmune response. Their bodies trigger the response against all cells producing a foreign cytotoxic spike protein which the immune system does not recognize.
Furthermore, heart tissue damaged during the attack by the immune system does not regenerate and, when untreated, the damage is permanent and, in this regard, the only way that such damage can be corrected is via the pathway of repair vs. regeneration; hence, the role played by scar tissue (advancing or otherwise) following irreversible damage caused to myocardiocytes.
This scarring, and the other immunoinflammatory pathophysiological processes involved in the development and progression of periodontitis are similar to those observed in myocarditis, and it is this similarity that provoked the recognition of the possible presence of therapeutic or mechanistic foci that could be taken advantage of in the creation of different treatment approaches for either or both periodontitis and myocarditis (Cardoso EOC, Fine N, Glogauer M, Johnson F, Goldberg M, Golub LM and Tenenbaum HC (2021) The Advent of COVID-19; Periodontal Research Has Identified Therapeutic Targets for Severe Respiratory Disease; an Example of Parallel Biomedical Research Agendas. Front. Dent. Med. 2:674056. Doi: 10.3389/fdmed.2021.674056).
Based on this evidence, and after reviewing all of the other pertinent data, Dr. Chris Shoemaker stated that approximately 20% of the vaccinated population will suffer from myocarditis. Approximately 50% of this group will most likely be dead within the next five years and 75% within the next ten years. This is a very conservative estimate, and this Substack has previously established that there were marked differences between the “vaccine” hot lots vs deliberately inactive lots; to wit:
CDC confirms 100% of reported Covid-19 Vaccine Deaths were caused by just 5% of batches produced & the majority were sent to red Republican States across the USA
·
FEB 19
The recent revelations of ubiquitous plasmid DNA contamination of the COVID-19 injections makes it clear that at very least 20% of the injected population will suffer heart-damaging autoimmune response.
Which brings us to bombshell research of Dr. Howard Tenenbaum, a highly credentialed Canadian scientist who was the Dentist-in -Chief, Sinai Health, and Head of the Division of Research in the Department of Dentistry at Mount Sinai Hospital in Toronto. He is currently a member of the Department of Dentistry at Mount Sinai Hospital since 1984.
Dr. Tenenbaum is a Professor of Periodontology and was head of that discipline for eight years (1997-2005) at the Faculty of Dentistry, University of Toronto. He has also served as Associate Dean for Biological and Diagnostic Sciences in that Faculty.
Dr. Tenenbaum is a cross-appointed Professor in the Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathophysiology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Toronto. He is also a Professor of Periodontology at the School of Dental Medicine, Tel Aviv University, Israel.
Dr. Tenenbaum has had a unique career as a periodontist, teacher and dental researcher, pursuing ongoing research in the fields of bone cell biology, periodontology, the relationships between oral inflammation and systemic diseases as well as ongoing studies in orofacial pain. He has published more than 300 research papers, and has also published book chapters and abstracts in major scientific and clinical journals. In addition, Dr. Tenenbaum has been invited to lecture nationally and internationally in his various areas of interest.
Dr. Tenenbaum has been awarded an Alumnus of Distinction Award from the University of Toronto Faculty of Dentistry, and fellowships with the American College of Dentists, Academy of Dentistry International, Pierre Fauchard Academy and International College of Dentists.
Dr. Tenenbaum has also been granted Honorary Induction into Omicron Kappa Upsilon from the International Honours Dental Society.
Dr. Tenenbaum’s decades of research and practical experience in administering doxycycline to repair or inhibit tissue injury in the periodontium (e.g., gums), led to his interest in the potential for the administration of doxycycline for heart injury management. Dr. Tenenbaum has put forward a model for a potentially novel approach to treating myocarditis with a combination of doxycycline, ivermectin, zinc and resveratrol. His research suggests that a low dose of doxycycline could prove to be a preventative measure for myocarditis, and a full dose for symptomatic myocarditis.
Which brings us to today’s exclusive research paper graciously provided to this Substack by Dr. Tenenbaum, marking the first time that this lifesaving work is being shared publicly.
Possible Treatment Approach for Management of Post-COVID Vaccination Myocarditis
Author: Howard Tenenbaum DDS, Dip Perio, PhD, FRCD(C)
Date: October 24, 2023
Title: Possible Treatment Approach for Management of Post-COVID Vaccination-Induced Myocarditis
Abstract:
Myocarditis is an inflammatory disease of the heart muscle, and this inflammation can also include the pericardium singly or together. These conditions, particularly myocarditis, that can lead to a variety of complications, including heart failure and arrhythmias, a large percentage of which can be fatal. The exact cause of myocarditis is often unknown, but it is thought to be triggered by a viral infection or an immune reaction suggesting autoimmunity is involved to some degree. In addition to muscle damage itself, it should also be recognized that following this damage, the heart muscle is incapable of regenerating. This leads ultimately to the development of scar tissue, which when severe can advance to a point where early incapacitation, need for heart transplant or death occurs within 5-10 years following onset of myocarditis.
Current treatments for myocarditis are primarily focused on reducing inflammation and preventing further damage to the heart muscle. However, these treatments are not always effective, and there is a need for new therapies that can more effectively target the underlying causes of the disease.
Recent research has shown that compounds with anti-inflammatory and anti-matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) properties may be promising candidates for the treatment of myocarditis. MMPs are a family of enzymes that are involved in the breakdown of the extracellular matrix (ECM). The ECM is a network of proteins that provides structural support for cells and tissues. In myocarditis, MMPs can contribute to inflammation and damage to the heart muscle.
Doxycycline, a tetracycline antibiotic, is one such compound with anti-MMP properties. When used at lower doses than those typically used for antibiotic purposes, it can inhibit certain metalloproteinases while not giving rise to antibiotic resistant bacteria. This property has led to its investigation as a potential therapy to reduce tissue damage in conditions where metalloproteinase activity is a concern.
Oxidative Stress
Although not a central focus of this article we also point out that oxidative stress plays an important role in the progression of myocarditis (and CHF). This is important since use of agents with antioxidant activities (e.g., doxycycline, resveratrol) could also be helpful (and will be discussed in another Substack article).
Parallel Disease Model-Experimentally Induced Congestive Heart Failure
In an early investigation, our group used a broad-spectrum inhibitor (CP-471,474 - Pfizer) led to a 50% reduction in the development of experimentally induced post-MI heart failure. This agent was used as it was considered more specific (from a mechanistic/investigational point of view) than doxycycline (https://tspace.library.utoronto.ca/bitstream/1807/111723/1/mr02197_ocr.pdf) most particularly since it has no known antioxidant effects meaning that its impact on CHF in this model could be more likely ascribed to inhibition of MMPs and not to antioxidant effects. As shown below, the inhibition of MMP activity led to reductions in congestive heart failure that are comparable to the effects of an ACE inhibitor. Notably, from a clinical perspective doxycycline could be used instead (see other studies re myocarditis below) and has fewer side effects than CP-471, 474 and is, moreover, approved for safety already. Furthermore, doxycycline has antioxidant properties, and it is also known that oxidative stress also plays an important role in the progression of CVD and in this regard, doxycycline’s antioxidant effects would be beneficial too and is of particular importance as well, since CP-471 is not known to have antioxidant properties as alluded to above.
The combination of anti-inflammatory and anti-MMP compounds may be a particularly effective approach to the treatment of myocarditis. By targeting both inflammation, oxidative stress and MMP activity, these compounds may be able to more effectively prevent damage to the heart muscle and to promote healing. Below, the data demonstrates the inhibition of MMP activity reduces CHF parameters by about 50% compared to control and is as effective as the ‘gold standard’; an ace inhibitor.
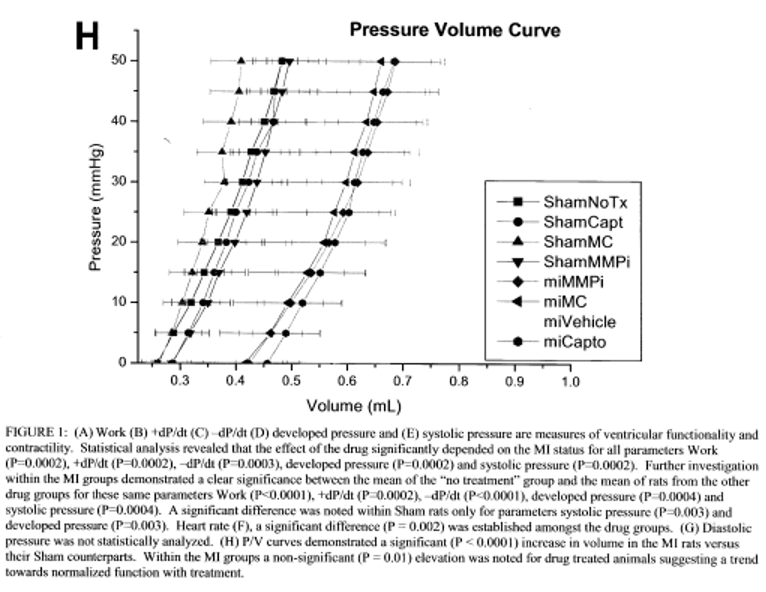
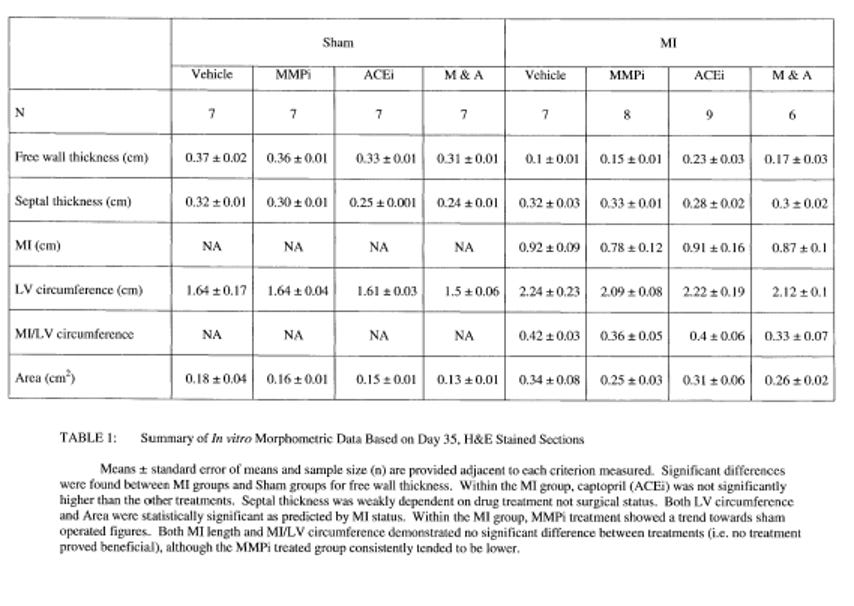
When taking into account studies focused on MMP activity and myocarditis along with our earlier findings relating to damage to the heart and development of CHF, there is every reason to anticipate that MMP inhibition (as well as inhibition of oxidative stress which will be addressed at a later time) could prove to be a useful therapeutic tool for the management of myocarditis and its sequelae. We suggest that MMP inhibition, reduction of oxidative stress and modulation of other inflammatory system components that exacerbate inflammatory heart disease could be accomplished by use of a multi-drug repurposed drug approach.
Discussion:
The following compounds have been shown to have anti-inflammatory and anti-MMP properties, including doxycycline:
Ivermectin
Resveratrol
Zinc
Tetracyclines (including doxycycline)
These compounds have demonstrated benefits in various preclinical models of disease, including myocarditis. For instance, ivermectin has been shown to reduce inflammation and improve heart function in a mouse model of viral myocarditis. Resveratrol has decreased MMP activity and enhanced heart function in a rat model of autoimmune myocarditis. Zinc has lowered inflammation and improved heart function in a rat model of doxorubicin-induced myocarditis. Tetracyclines, including doxycycline, have diminished MMP activity and improved heart function in a mouse model of pressure overload-induced myocarditis.
The combination of these compounds may represent a promising approach to the treatment of myocarditis. By concurrently addressing inflammation and MMP activity, these compounds may more effectively prevent heart muscle damage and facilitate healing.
Clinical trials are essential to assess the safety and efficacy of these compounds in myocarditis treatment. However, the preclinical data suggest that these compounds may serve as promising candidates for the development of new therapies for this condition.
Conclusion:
The combination of anti-inflammatory and anti-MMP compounds, including , may hold potential as a therapy for myocarditis. These compounds have shown benefits in preclinical models of the disease and may be capable of preventing heart muscle damage and promoting healing more effectively. Clinical trials are warranted to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of these compounds
in the treatment of myocarditis.
Deploying a combination therapy against the iatrogenic myocarditis outbreak consisting of inexpensive repurposed drugs doxycycline and ivermectin may be the only truly effective strategy currently available to reverse this condition.
The overlap between the myocarditis combination therapy and the turbo cancer combination therapy is no coincidence considering that both diseases are caused by the interactions of DEATHVAX™ payload mechanisms.’



Oxidative stress, hummh? Vitamin C might be effective as well.
They just need to add ascorbate, L-ribose, and CoQ10 to the protocol!